2025 is set to be a turning point for the packaging industry, propelled by groundbreaking solutions emerging to meet the requirements of the PPWR—Europe’s latest regulation (2025/40) from the European Parliament and the EU Council dated 19 December 2024 on packaging and packaging waste. Although it officially came into force on 11 February, its provisions won’t take effect until 12 August 2026. Companies that choose to get ahead of the curve by investing in greener packaging options are poised to lead the market, satisfy shifting consumer expectations, and actively drive the transition to a more efficient and responsible circular economy.
Regulatory context and industry challenges
European and national sustainability directives have grown increasingly strict. The “Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation” (PPWR)” sets ambitious goals for recyclability, reusability, and reducing single-use plastics. As a result, companies are being driven to rethink their packaging strategies to lower their environmental impact and comply with these new requirements.

The key challenges posed by this regulation will shape the trends that define the sector in 2025 and beyond.
1. Reducing plastic use and increasing recycled content (articles 6 and 7) One of the core measures in the PPWR focuses on drastically cutting virgin plastic consumption. The regulation mandates that all plastic packaging contain a minimum percentage of recycled plastic, with step-by-step targets set through 2030. This move is expected to boost the development of advanced recycling technologies and spur the creation of next-generation biodegradable plastics.
2. Mandatory recyclability and reuse (articles 6, 10)
The regulation requires all packaging to be designed for economically viable recycling by 2030. This will bring renewed attention to how packaging is conceived, encouraging simpler solutions and, where possible, single-component materials that make sorting and recycling more efficient. In addition, the PPWR promotes reuse and refill systems—especially in the food and beverage sector—by setting binding targets for reusable packaging.
3. Harmonized labeling and consumer transparency (article 12)
Another major change concerns the introduction of a uniform labeling system across Europe, aimed at improving waste sorting and reducing consumer confusion. This system will help clearly identify the materials used in packaging and the proper disposal methods, encouraging more responsible behavior.
4. Innovative materials and compostable packaging (articles 8 and 9)
The new rules also push for the adoption of innovative and biodegradable materials. The compostable packaging segment is set to grow rapidly, thanks to solutions designed to minimize contamination in organic waste streams. However, the PPWR indicates that compostable packaging will be required only when it provides clear environmental benefits.
5. Curbing unnecessary packaging and cutting waste (article 10)
The regulation lays down strict limits on excessive packaging, requiring companies to minimize both weight and volume. This is likely to have a major impact on e-commerce, where packaging practices will be reevaluated to eliminate waste and enhance sustainability.
6. New producer obligations and financial incentives (article 45)
The regulation strengthens the principle of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), imposing higher costs on companies for the waste generated by their packaging. Businesses that switch to more sustainable materials and eco-friendly packaging methods may qualify for financial incentives and tax breaks.
We’ll have to wait and see how the sector adapts to these new challenges, but one thing is clear: the future of packaging is moving in a more sustainable direction, with innovation as its driving force.
The impact of consumers: sustainable packaging is shaping mass-market choices
According to Osservatorio Packaging of Nomisma 2025, sustainability has become a key factor in the food sector: for 7 out of 10 Italian consumers, it’s a decisive element when making purchase decisions.
For 46% of shoppers, packaging is even the main indicator of a product’s overall sustainability—topping local sourcing (43%) and low emissions (42%).

Consumers generally consider packaging sustainable if it’s fully recyclable (51%), kept to a minimum (43%), made with renewable materials (40%), and ensures low emissions (35%).
Meanwhile, more and more studies are highlighting potential health risks tied to unsustainable packaging, especially concerning microplastics, bisphenol, and PFAS.
As consumers become increasingly aware of the benefits for both the planet and their own well-being, manufacturers and major brands are naturally feeling the pressure to head in the same greener direction.
Technological innovations for sustainable packaging
Every year, millions of tons of plastic waste pile up in landfills and oceans, wreaking havoc on ecosystems.
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) recently published a report titled ‘Policy Scenarios for Eliminating Plastic Pollution by 2040,’ suggesting that integrated global policies tackling the entire lifecycle of plastics could reduce their environmental discharge by up to 96%.
Among the recommended measures are reducing plastic production and consumption, promoting eco-design, expanding recycling, and eliminating pathways by which plastics leak into the environment. Without more ambitious efforts than those underway, projections indicate that plastic production, usage, and waste will surge by 70% by 2040, with 19% of plastic waste destined to end up in nature.
The OECD’s call extends to institutions and the broader economic ecosystem—especially businesses, which have the potential to drive real change.
They’re being urged to innovate, because innovation—just as much as regulation—plays a vital role in creating alternatives to plastic, cutting waste, using fewer raw materials, lowering emissions, and ultimately pushing the industry toward a new concept of packaging with less environmental impact.
Digital technologies will definitely play a part. By 2025, smart packaging solutions will be on the rise across both food and pharmaceutical sectors, with IoT and AI set to take center stage. AI in particular is already proving its ability to inspire creative, custom-designed packaging: from smart containers that monitor food freshness and alert consumers to any issues, to packaging that offers personalized messaging or augmented reality experiences for a unique product encounter.

A notable AI-driven example comes from Amazon: its Package Decision Engine, a proprietary technology that ensures customer orders are shipped in the most appropriate, sustainable packaging—preventing damage and streamlining deliveries. It’s been in use across Europe and the U.S. for years and has already helped cut unnecessary packaging significantly, eliminating over 2 million metric tons of packing materials.
Of course, new materials will also be a game-changer—especially biodegradable and compostable options with a lower environmental footprint, such as advanced bioplastics, high-strength recycled paper, and algae-based or food-waste-derived coatings. Some of these solutions are more mature, while others need further refinement or proof they can match the required functionality, cost-effectiveness, and overall sustainability.
Among these up-and-coming materials is Qwarzo®, a coating that’s quickly earning ‘game-changer’ status.
The sustainable value of Qwarzo®
Qwarzo® is an innovative mineral-based coating engineered to significantly enhance the performance of the materials it’s applied to.
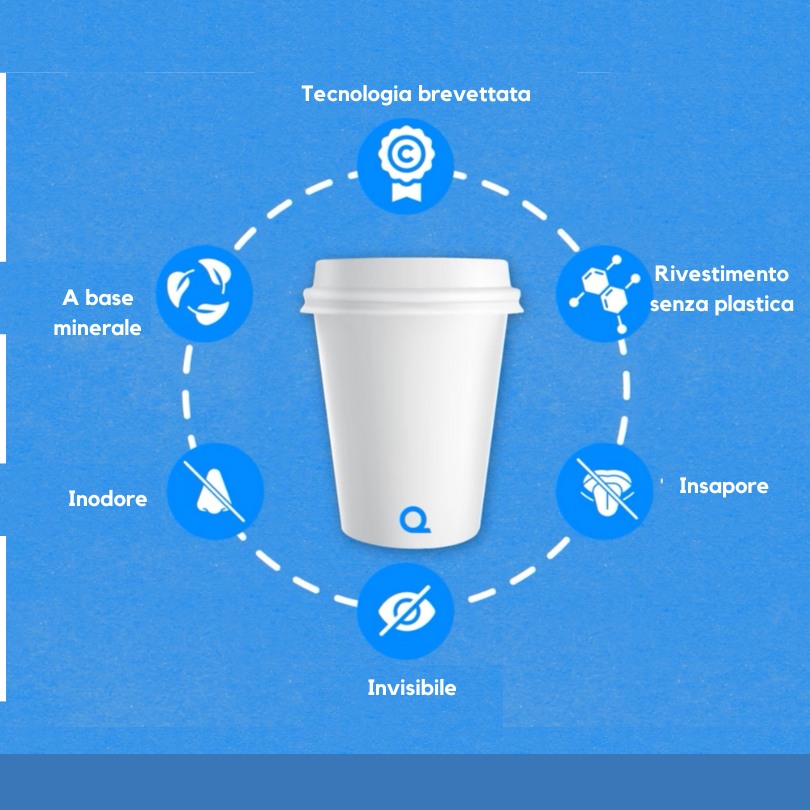
Thanks to its ability to bond seamlessly with the substrate, it strengthens key properties without hindering recyclability. One standout feature is the absence of plastics and PFAS, which helps safeguard the quality of recycling and actively reduce environmental impact.
Qwarzo® is fully odorless, tasteless, and invisible, yet it provides remarkable strength that meets modern packaging demands. In the food industry, it offers reliable protection while preserving the character of the underlying material, so it never interferes with flavors. At the same time, it shields the package or product from fats, water, high temperatures, and aggressive chemicals, and it acts as a solid barrier against oxygen and vapor—helping keep products fresh and high-quality.
Its versatility and easy integration into industrial processes mean Qwarzo® can be applied to a wide range of packaging materials, spanning everything from food to cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. This flexibility makes it both highly scalable and economically sustainable.
As a result, Qwarzo® is now emerging as a real-world, forward-thinking solution for the food packaging industry, offering an effective and safe way to cut back on plastic coatings without sacrificing the performance that today’s market demands. By aiding in the shift toward a circular economy, it’s poised to become a true turning point for the future of sustainable packaging.



